What is a vapor chamber heatsink?
When your CPU or GPU heats up under pressure, how do you stop it from frying? Regular heatsinks often fall short-and that’s where vapor chamber heatsinks come in.
A vapor chamber heatsink is a flat, sealed heat spreader filled with a small amount of liquid that evaporates and condenses to rapidly move heat away from hot components.
It’s a simple idea with powerful impact. Let’s break down exactly how vapor chambers work, how good they are, and how they compare to other methods like liquid cooling.
What is a vapor chamber heatsink?
When computers or machines run, they create heat. That heat needs to move away fast or things get damaged. Traditional metal heatsinks aren’t always good enough. Vapor chambers fix that. They move heat fast and evenly.
A vapor chamber is a thin, sealed metal container that uses phase change-evaporation and condensation-to spread heat more effectively than solid metal alone.
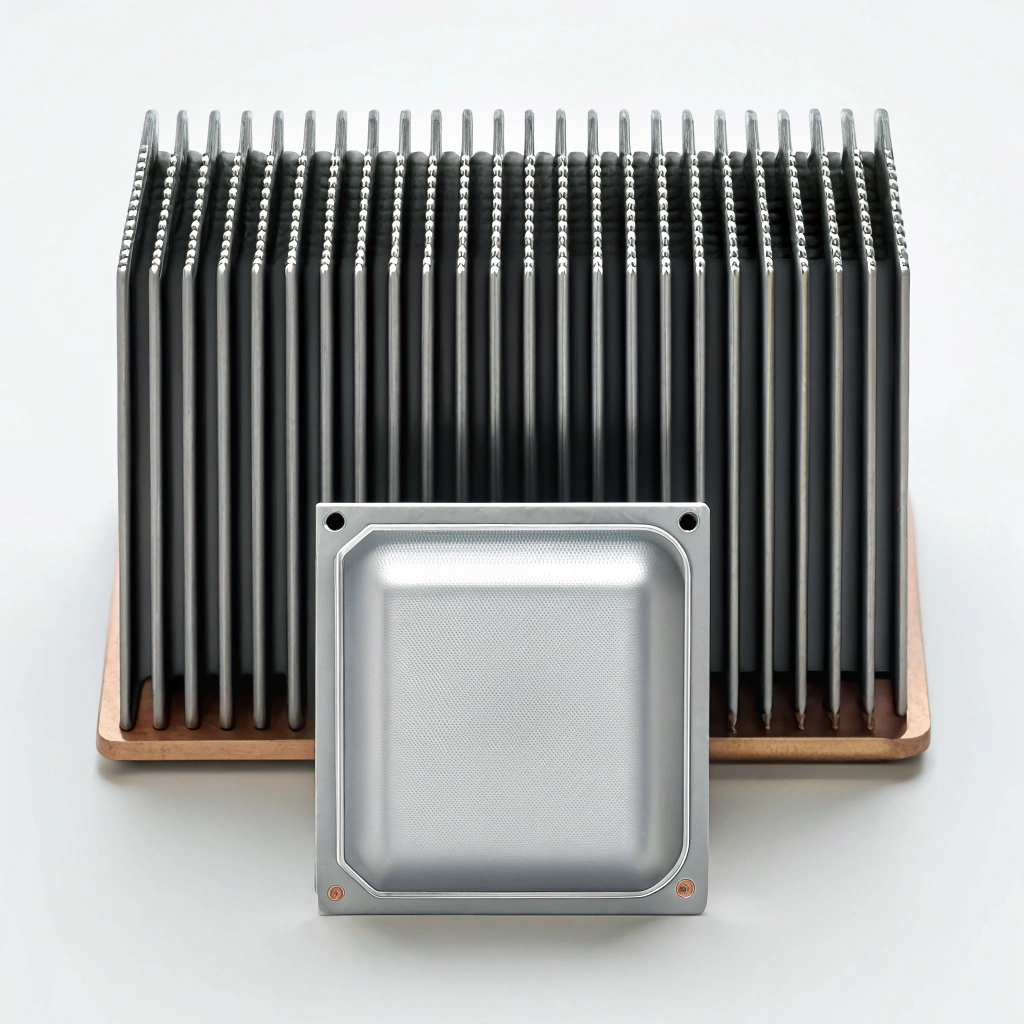

Let me explain how it works:
- Inside the chamber is a small amount of working fluid-usually water.
- When the device gets hot, this liquid turns into vapor.
- The vapor rushes to the cooler sides of the chamber.
- There, it cools and turns back into liquid.
- A special wick pulls the liquid back to the hot area.
- The cycle repeats-nonstop.
Key parts inside a vapor chamber
| Komponenta | Funkce |
|---|---|
| Working fluid | Evaporates at heat source, condenses at cool areas |
| Metal container | Usually copper, conducts heat and seals the system |
| Wick structure | Guides liquid back to the heat source |
This setup allows heat to move quickly and evenly across a large flat surface. It’s like turning a small flame into a wide, smooth glow-great for spreading heat across processors, graphics cards, and even smartphone chips.
A vapor chamber uses only solid metal and no liquid inside.False
Vapor chambers rely on internal liquid to evaporate and condense, moving heat efficiently.
The wick inside a vapor chamber helps return liquid to the heat source.Pravda
The wick guides condensed liquid back to where heat is generated, allowing the cycle to repeat.
How good is vapor chamber cooling?
Sometimes I get asked, "Is it really worth the extra cost to get vapor chamber cooling?" The answer often comes down to your performance needs and design limits.
Vapor chamber cooling is highly efficient for compact, high-performance electronics where space is tight and heat spread needs to be even.

Vapor chambers don’t just cool-they spread heat across surfaces. That means:
- No hotspots under your CPU or GPU.
- Lower overall temperature.
- More stable system performance.
Let’s look at where this matters:
Ideal use cases:
- Gaming laptops: Powerful but slim, with little room for bulky cooling systems.
- Chytré telefony: High-density chips packed in small areas.
- High-performance servers: Where airflow is tight and surfaces are dense.
- Průmyslové stroje: Where silent, sealed solutions are a must.
In these settings, the vapor chamber does the job of several heat pipes in a much thinner package.
Benefits over traditional cooling
| Funkce | Výparná komora | Solid Metal/Heat Pipes |
|---|---|---|
| Šíření tepla | Extremely even | Uneven, can create hotspots |
| Response time | Fast (phase change) | Slower (pure conduction) |
| Tloušťka | Thin and flat | Bulkier, shaped around pipes |
| Spolehlivost | No moving parts | Same, but less efficient |
This uniform performance is why phone makers and laptop brands now use vapor chambers more often. When everything runs cooler, battery lasts longer, fans spin less, and your device lives longer.
But vapor chambers are not magic. They have a cooling limit. If your system generates too much heat continuously-say in a workstation or gaming PC with high wattage-they might not handle it alone.
Vapor chambers cool devices by distributing heat with liquid movement and evaporation.Pravda
The working liquid evaporates and condenses to carry heat across the surface.
Vapor chamber cooling is only useful in large desktop computers.False
Vapor chambers are most useful in compact designs like laptops and phones.
Is vapor chamber cooling better than liquid cooling?
Many customers ask, "Should I choose vapor chamber or go for full liquid cooling?" That depends on your system, space, and thermal demand.
Vapor chambers are better for compact, silent, and low-maintenance setups, while liquid cooling is better for maximum heat removal.
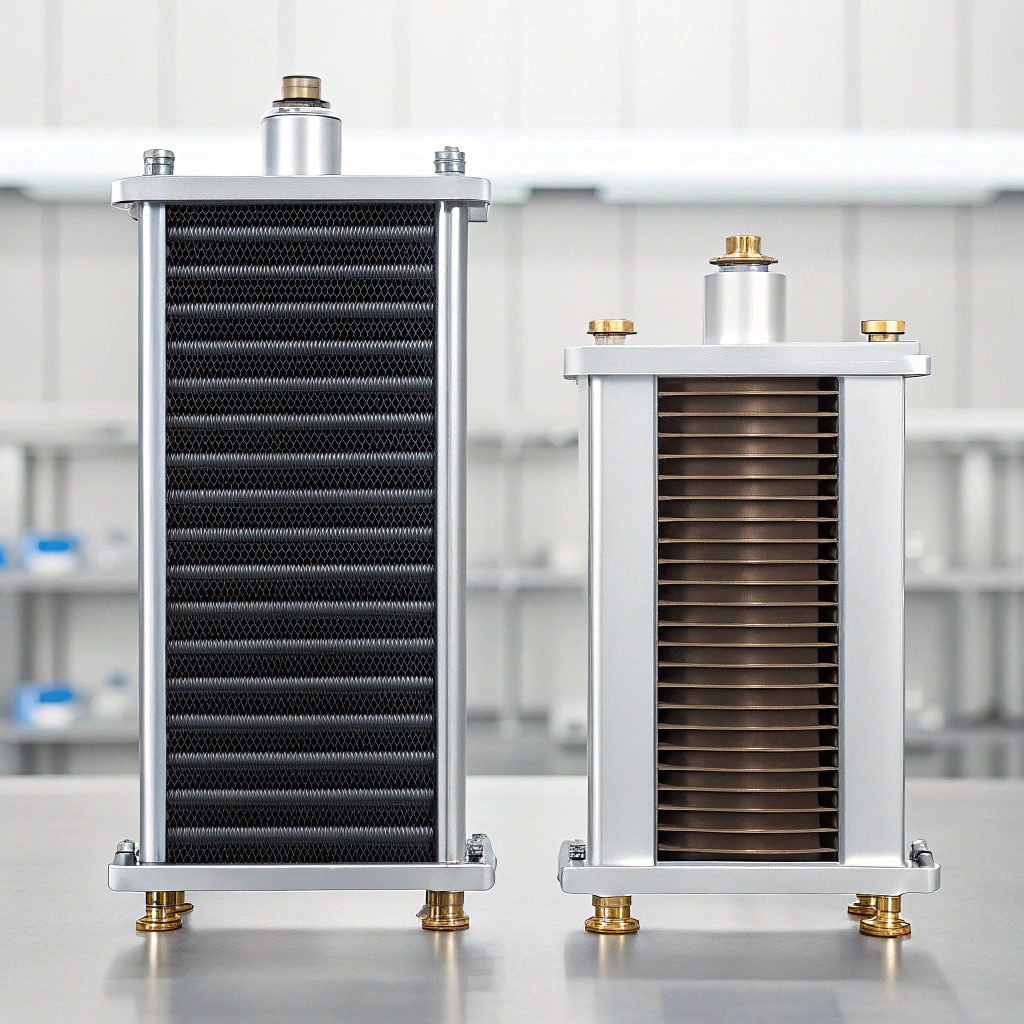

Let’s compare key features:
Výparná komora
- Flat, sealed: No tubes, pumps, or fans.
- Silent: No moving parts.
- Reliable: No leaks or maintenance needed.
- Slim profile: Perfect for thin devices.
- Fast response: Handles thermal spikes well.
Kapalinové chlazení
- High capacity: Moves lots of heat, great for gaming or overclocking.
- Custom loops: You can design flow paths.
- Fans and pumps: Needs airflow and coolant movement.
- Risk of leaks: Especially in older or DIY setups.
- Bulkier design: Needs room for radiator and tubing.
Srovnávací tabulka
| Funkce | Výparná komora | Kapalinové chlazení |
|---|---|---|
| Chladicí výkon | Mírná až vysoká | Velmi vysoká |
| Space requirements | Very compact | Requires significant space |
| Noise level | Silent | Often noisy due to fans/pumps |
| Údržba | Žádné | Requires occasional maintenance |
| Risk of failure | Velmi nízká | Moderate (leaks, pump wear) |
If you’re building a high-end PC and don’t mind maintaining a loop, liquid cooling will outperform. But if you’re making laptops, handhelds, or servers where you want peace of mind and small form, vapor chambers are better.
Liquid cooling systems require pumps and fans to circulate coolant.Pravda
They use moving parts to move coolant through tubes and radiators.
Vapor chambers are usually louder and harder to install than liquid systems.False
Vapor chambers are silent and easy to integrate into flat surfaces.
What are the disadvantages of a vapor chamber?
Vapor chambers are not perfect. While they offer many benefits, there are also trade-offs. You need to understand them before making a final choice.
Main disadvantages include higher cost, performance limits under extreme loads, sensitivity to orientation, and eventual wear over time.

Let’s break down the key limitations:
1. Higher cost
- Vapor chambers are more expensive to manufacture than traditional heatsinks or heat pipes.
- The wick and sealed structure require precision.
- For low-budget builds, this can be a dealbreaker.
2. Heat load ceiling
- Vapor chambers can only handle so much heat.
- Beyond a certain power level (like high-end overclocked CPUs), they may reach saturation.
- Unlike liquid cooling, they don’t scale up easily.
3. Orientation sensitivity
- In vertical setups, gravity can affect wick function.
- Most work best when relatively flat (less than 15-degree tilt).
- This matters in industrial or rackmount server environments.
4. Lifespan and wear
- Over time, the wick can degrade or clog.
- The sealed system may lose vacuum or working fluid.
- While it takes years, long-term performance can drop.
Summary Table: Pros and Cons
| Výhoda | Omezení |
|---|---|
| Efficient, even cooling | Vyšší počáteční náklady |
| Silent and reliable | Cannot handle extreme heat loads |
| Ideal for compact devices | Orientation affects performance |
| Zero maintenance | Limited long-term performance stability |
Despite these downsides, most vapor chambers last for many years under normal use. They’re trusted by major brands in phones, laptops, and data centers for a reason.
Vapor chambers can suffer reduced efficiency if used at steep angles.Pravda
Gravity affects the return flow of liquid in the wick structure.
Vapor chambers are cheaper and simpler to make than standard heat pipes.False
They cost more due to complexity and manufacturing precision.
Závěr
Vapor chamber heatsinks offer quiet, efficient, and space-saving cooling solutions for modern electronics. While not ideal for extreme heat loads, they shine in compact and precision-critical applications. From smartphones to server blades, they keep things cool-silently and reliably.


 Mám pocit, že při rozhodování o tom.](https://sinoextrud.com/wp-content/uploads/auto_1756203839_1.webp 1024w, https://sinoextrud.com/wp-content/uploads/auto_1756203839_1-768x768.webp 768w, data:image/webp;base64,UklGRm4AAABXRUJQVlA4IGIAAAAQAgCdASoMAAwAAQAaJZwCw7ELT8mHaVAAAP71B+5k9/8OIH4ljai97rwcFQdPt63h/dFxP826lG4t8v06aMcrTG3tJJQwoTgUvWYyxDaPWA9hETv9WrDiFuqjrDA77AAAAA== 12w, https://sinoextrud.com/wp-content/uploads/auto_1756203839_1-600x600.webp 600w)
