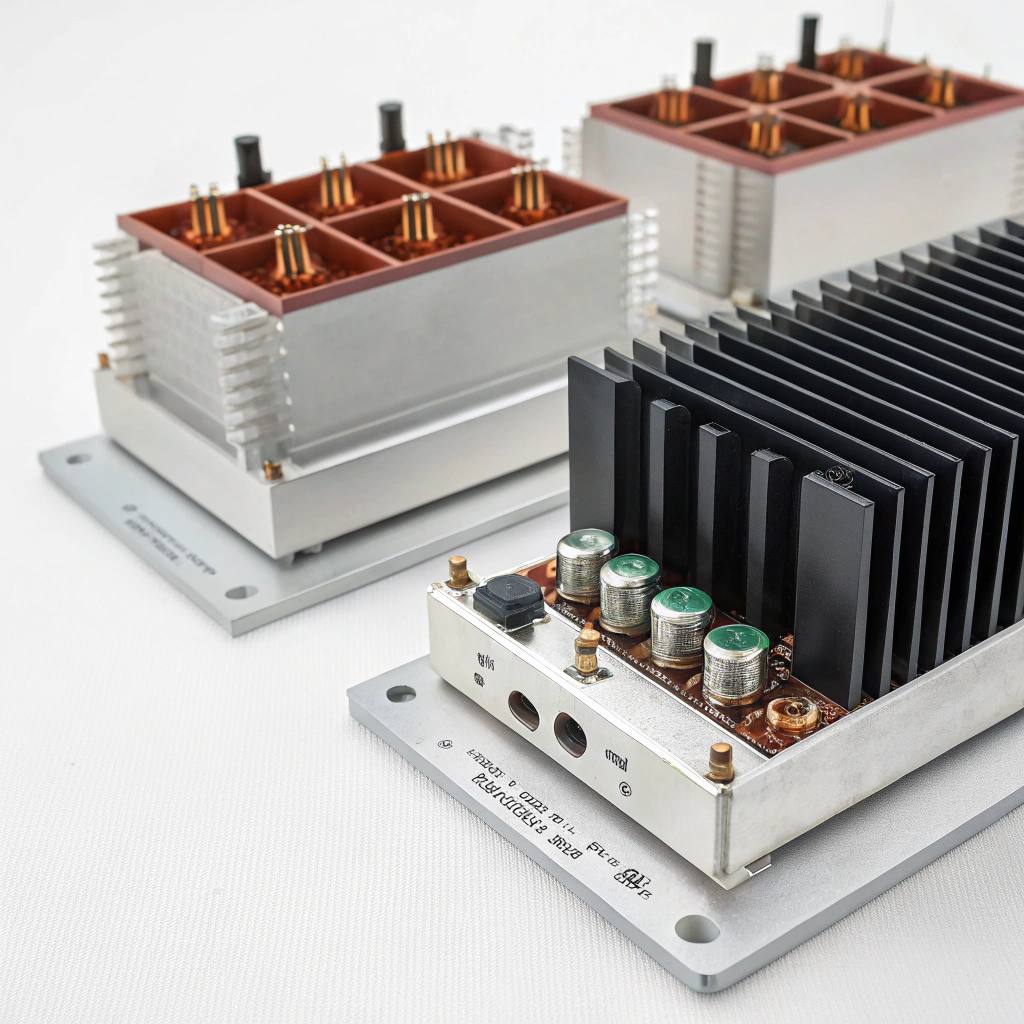
7 Key Factors to Consider When Sourcing Industrial Heat Sinks from Overseas Suppliers
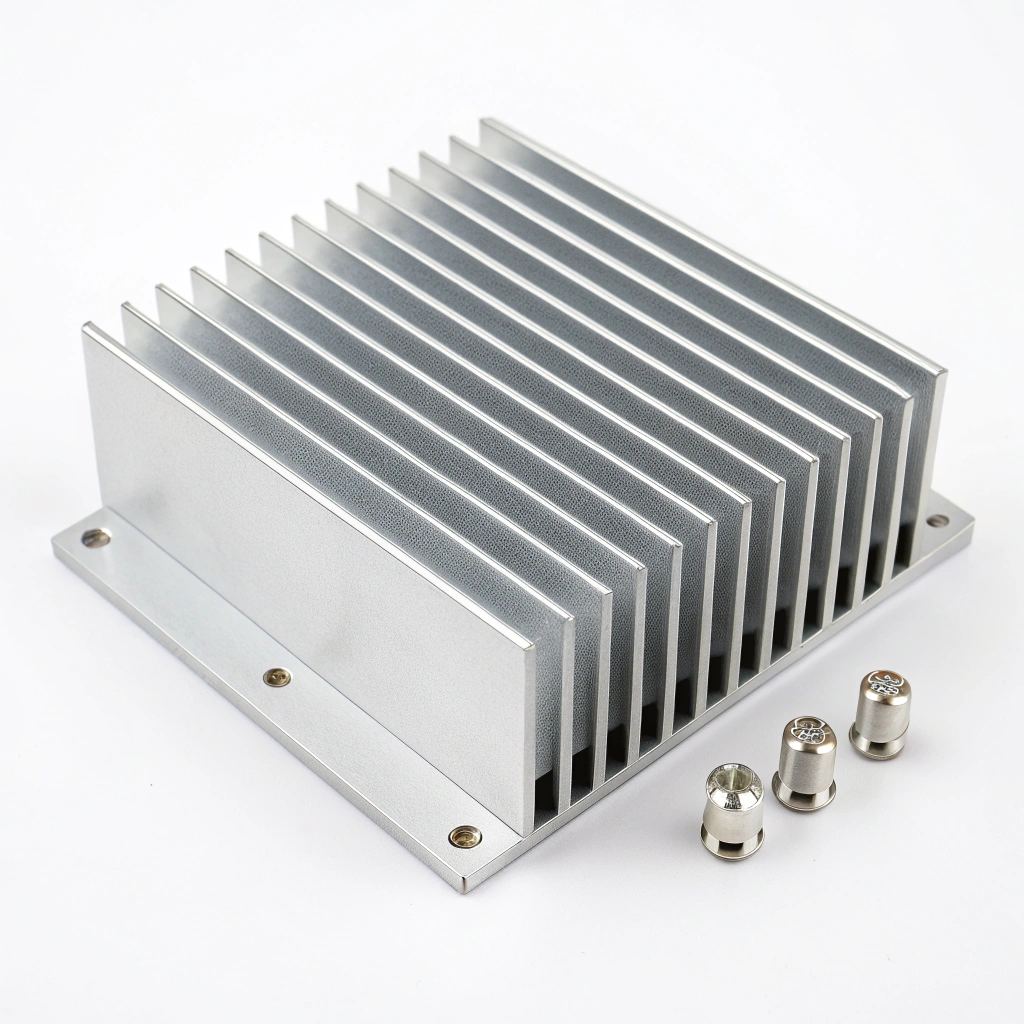
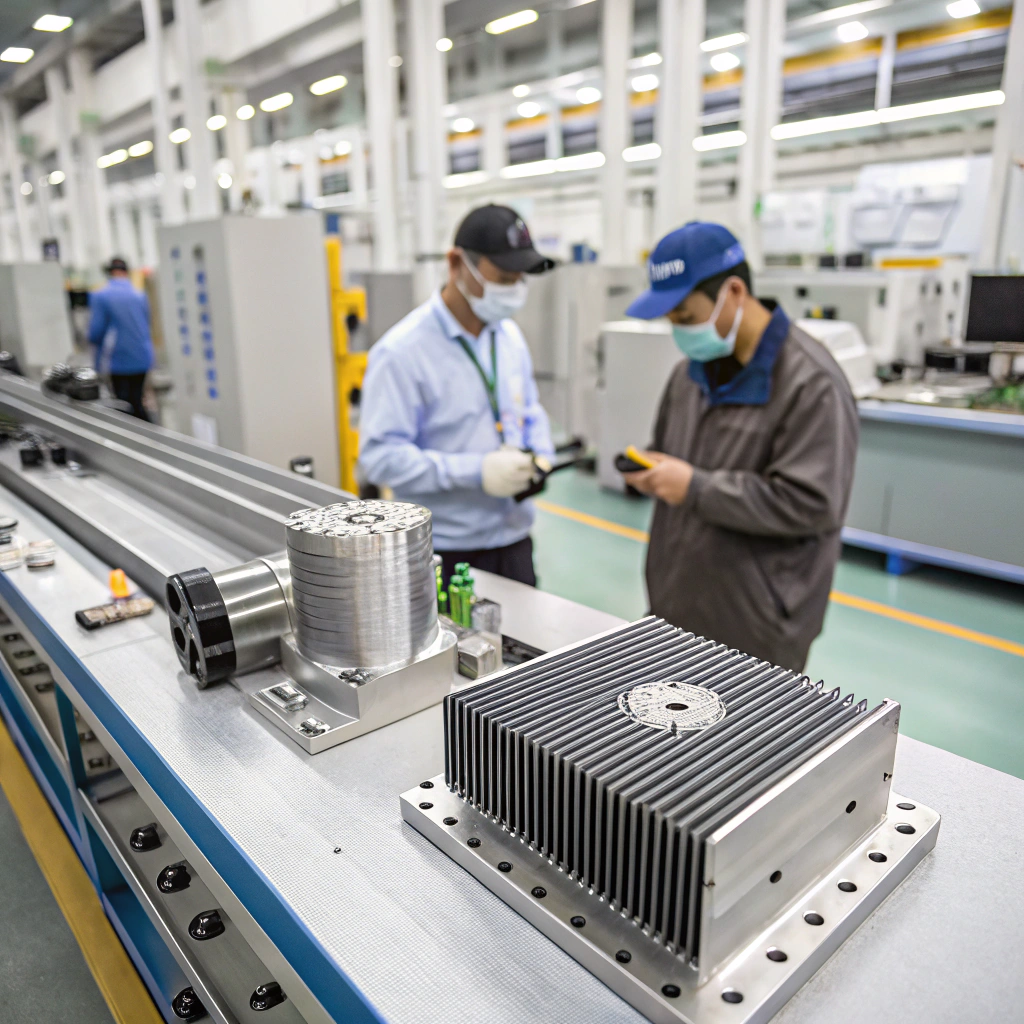
When we work with procurement teams sourcing industrial heat sinks overseas, we see the same challenges repeat: inconsistent thermal performance, drawings that don’t match delivered parts, and long lead times that quietly disrupt production schedules. In our experience as an aluminum extrusion manufacturer, heat sinks look simple—but overseas sourcing exposes risks that only show up after parts are already on the water.
Our team has learned that buyers who focus only on unit price usually pay more later. Tool revisions, rejected batches, or unstable thermal results quickly erase any initial savings. That’s why we always encourage customers to evaluate overseas heat sink suppliers through a much broader, engineering-driven lens.
Below are the 7 key factors we recommend every buyer evaluate before committing to an overseas industrial heat sink supplier.
1. Can the Supplier Actually Meet Your Thermal Performance Requirements?
When buyers approach us, the first thing we ask is not price—it’s thermal target. We often see RFQs that specify dimensions but omit required thermal resistance (°C/W), airflow assumptions, or operating environment.
In our experience, serious suppliers will reference accepted design data, such as aluminum thermal conductivity benchmarks published by NIST
aluminum thermal conductivity reference data.
If a supplier cannot explain how fin geometry, alloy choice, and surface treatment affect heat dissipation, we consider that a red flag. We recommend working only with suppliers who validate performance before mass production.
2. Are Alloy Selection and Extrusion Standards Clearly Defined?
We frequently see overseas disputes caused by vague alloy descriptions like “6063 aluminum” without temper, tolerance class, or applicable standard. In practice, that ambiguity invites substitution.
We always recommend locking specifications to recognized extrusion standards such as ASTM B221
ASTM aluminum extrusion specification.
For European projects, we also align with EN 755 requirements
EN 755 aluminum extrusion tolerances
Clear alloy and standard definitions protect both thermal performance and dimensional consistency.
3. Does the Supplier Control CNC Machining and Flatness In-House?
In our experience, heat sink performance often fails not because of extrusion, but because of poor secondary machining. Uneven mounting surfaces increase thermal resistance dramatically.
We advise buyers to confirm whether CNC machining is handled in-house or outsourced. In-house control allows the supplier to manage flatness, perpendicularity, and repeatability.
Suppliers who reference machining tolerances aligned with ISO 2768 general tolerances
ISO general machining tolerances
tend to deliver more consistent results over long production runs.
4. How Is Surface Treatment Controlled and Verified?
Surface finish is not cosmetic for heat sinks—it directly affects emissivity and corrosion resistance. We regularly see overseas shipments where anodizing thickness varies widely between batches.
We recommend requiring compliance with recognized anodizing standards such as ISO 7599 anodizing of aluminum standard.
Additionally, suppliers exporting into regulated markets must understand RoHS compliance requirements
RoHS substance restriction overview
Without documented surface control, long-term reliability is at risk.
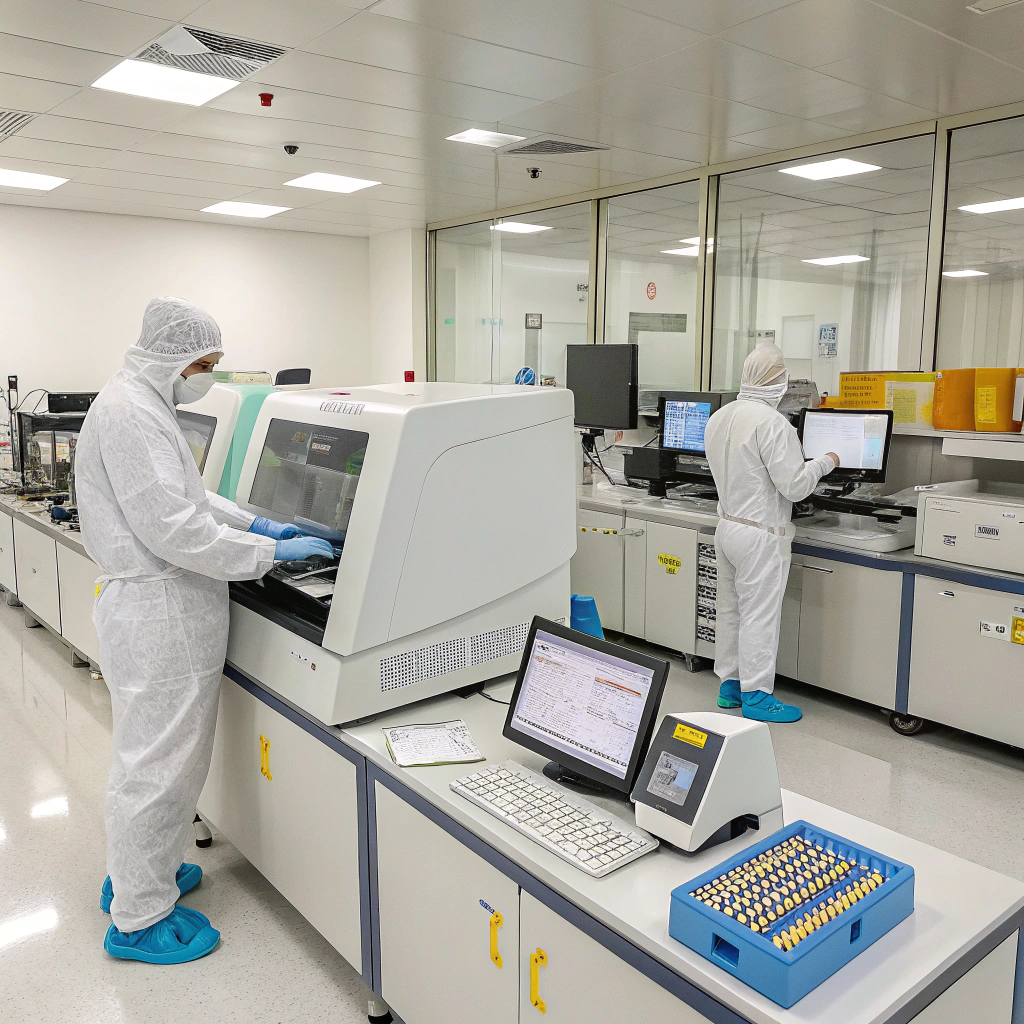
5. Are Quality Systems Auditable and Consistently Applied?
From our perspective, ISO certificates alone are not enough. What matters is how those systems are applied on the shop floor.
We recommend confirming active compliance with ISO 9001 quality management systems ISO 9001 quality management principles.
and, when sustainability matters, ISO 14001 environmental management
ISO 14001 environmental systems.
In our experience, buyers who request inspection reports, control plans, and batch traceability face far fewer surprises.
6. Are Logistics Terms and Lead Times Realistically Structured?
Overseas sourcing failures often happen after production is complete. We regularly help clients recover from poorly defined shipping terms.
We strongly recommend defining delivery responsibilities under official ICC Incoterms® rules Incoterms international trade definitions.
Clear Incoterms prevent disputes over freight, insurance, and customs clearance—especially critical for heavy aluminum shipments.
7. Does the Supplier Have Proven Experience with Industrial Applications?
Finally, we always ask buyers to look beyond sample quality and ask about application history. Heat sinks used in power electronics, inverters, or LED systems face very different stress profiles.
Suppliers familiar with guidance from organizations like the Aluminum Association aluminum heat sink design resources.
tend to understand how extrusion design, machining, and surface treatment interact in real-world industrial environments.
Conclusion
From our experience supplying industrial heat sinks globally, overseas sourcing can absolutely be cost-effective—but only when evaluated through engineering, quality, and logistics discipline.
When buyers address these seven factors upfront, we consistently see fewer delays, more stable thermal performance, and stronger long-term supplier relationships. That’s how overseas sourcing becomes a strategic advantage instead of a recurring operational risk.